
by Rich Benvin | Oct 14, 2025 | Breathing, Detox, Environment, Exercise, Inflammation, Integrative Medicine, Lifestyle Medicine, Lung Health, Mail Order Pharmacy, Mindfulness, Nutrition, Respiratory Health, Save Your Lungs
Conclusion & Afterword: The Breath of a New Beginning
Breathe to Heal: How Nutrition and Lifestyle Can Save Your Lungs
“Every breath you take is both an ending and a beginning — a release and a renewal.”
Your breath has carried you through every moment of your life — from your first cry to this very instant.
It is your most constant companion, yet the one you’ve likely noticed least.
Over the course of this book, you’ve learned that breathing isn’t just an automatic act — it’s a language.
Your lungs speak to every cell, organ, and emotion. They whisper balance when you’re still, strength when you move, and wisdom when you listen.
The path of Breathe to Heal isn’t about perfection — it’s about awareness.
Awareness of what you breathe in — the air, the thoughts, the emotions.
Awareness of what you breathe out — the tension, the toxins, the stories that no longer serve you.
Healing your lungs begins there.
🌿 1. The Cycle of Healing: From Surviving to Thriving
In the beginning, this journey may have been about recovery — from illness, inflammation, or exhaustion.
But now, it’s about something deeper: transformation.
You’ve learned how:
-
Food becomes the foundation of breath.
-
Movement opens space for oxygen to flow.
-
Breathwork harmonizes mind and body.
-
Environment and emotion shape how freely you inhale the world.
This isn’t just a health routine. It’s a philosophy — a rhythm of living that honors the intelligence of your body and the wisdom of your breath.
When you eat clean, breathe deeply, and live consciously, you are not just healing your lungs — you’re healing your connection to life itself.
💫 2. The Breath as a Mirror of Life
The breath is a mirror — reflecting who you are in this moment.
When you are anxious, your breath becomes fast and shallow.
When you are at peace, your breath becomes slow and deep.
When you are inspired, your breath expands — because inspiration literally means “to breathe in spirit.”
The state of your breath is the state of your being.
And the more you learn to guide it, the more you guide your destiny.
You have within you a tool that medicine cannot replicate — the ability to transform your inner chemistry with a single, conscious inhale.
The lungs respond instantly to love, gratitude, and stillness.
Each breath you take with awareness tells your body, “I am safe. I am healing. I am alive.”
🧘 3. Breath, Awareness, and the Present Moment
In every culture, from the yogis of India to the Taoist masters of China to the modern neuroscientists of today — the truth remains the same:
The breath anchors you to now.
You cannot breathe in the past or the future.
Each inhale is a return to the present — the only moment where healing ever happens.
If you take one lesson from this book, let it be this:
Whenever life feels chaotic, uncertain, or overwhelming… pause and breathe.
Return to the rhythm that sustains you.
The body remembers how to heal when the mind remembers how to be still.
💨 4. Living the “Breathe to Heal” Way
Going forward, think of this book not as something to finish, but as something to live.
🌱 Eat with purpose. Choose foods that nourish your lungs and bring you energy rather than inflammation.
🏃 Move with awareness. Let every step, stretch, or twist be a celebration of your ability to breathe.
🌬️ Breathe consciously. Even five minutes a day can transform your mood, focus, and health.
🌙 Rest deeply. Sleep is the lungs’ quiet regeneration. Protect it like sacred time.
🌎 Protect your environment. Clean air, sunlight, and nature are your daily medicine.
💗 Connect and feel. Your lungs expand when your heart does — through laughter, empathy, and love.
Each of these is a form of breathing — an exchange with the world that brings balance, clarity, and strength.
🌺 5. From Breath to Purpose
Ultimately, this book is about rediscovery.
Rediscovering that health is not something you chase — it’s something you create.
That wellness isn’t a pill — it’s a pattern.
That the simple act of breathing consciously is one of the most profound forms of prayer.
When you choose to live in rhythm with your breath, you align yourself with life’s natural intelligence — the same intelligence that grows forests, heals wounds, and makes the heart beat.
You are not separate from that intelligence. You are it.
🌈 6. The Final Breath (and the First of Many)
Take one deep, conscious breath right now.
Feel it enter your lungs, fill your body, and expand your awareness.
Hold it for a moment — feel its life-giving power.
Then exhale slowly, letting go of what no longer serves you.
That’s all healing really is — the continual rhythm of release and renewal.
Let every breath remind you of this truth:
You are not broken. You are breathing — and that means you are becoming whole.
The journey doesn’t end here.
It begins with your next inhale.
🕊️ Author’s Note
This book is dedicated to everyone who has ever struggled to catch their breath — literally or metaphorically.
May it remind you that the breath you seek is already within you, waiting to be heard, honored, and healed.
Breathe gently.
Breathe bravely.
Breathe to heal.


by Rich Benvin | Oct 14, 2025 | Breathing, Detox, Exercise, Inflammation, Lifestyle Medicine, Lung Health, Mail Order Pharmacy, Mindfulness, Nutrition, Respiratory Health, Save Your Lungs
Chapter 12: Recovery and Regeneration — Healing from Infection, Inflammation, and Chronic Lung Damage Naturally
Breathe to Heal: How Nutrition and Lifestyle Can Save Your Lungs
“Healing is not about going back — it’s about becoming whole again.”
Respiratory illnesses — whether viral, bacterial, or chronic — can leave deep imprints on the body.
Even after symptoms fade, inflammation, scarring, and fatigue may persist for months or years.
But here’s the truth that modern research now confirms: the lungs can regenerate.
Given the right conditions, the body can repair damaged airways, rebuild alveoli, and restore oxygen capacity.
Healing is not just possible — it’s biological.
🫁 1. Understanding Lung Recovery: The Body’s Blueprint for Repair
Your lungs are remarkably resilient.
Inside them are over 480 million alveoli — microscopic air sacs responsible for oxygen exchange.
When these are damaged by infection or inflammation, nearby stem cells can activate to rebuild them.
Three stages of lung regeneration:
-
Repair: Inflammation resolves; old cells are cleared.
-
Regrowth: Stem cells divide to replace damaged tissue.
-
Remodeling: Collagen and elastin restore structure and flexibility.
Studies from Nature Medicine (2023) show that alveolar type II cells can regenerate up to 40% of lost lung tissue under supportive conditions — particularly when inflammation and oxidative stress are controlled.
The right nutrition, oxygenation, and rest accelerate this process.
🔥 2. Post-Inflammatory Healing: Cooling the Fire Within
After infection or chronic irritation (like asthma, bronchitis, or pollution exposure), the lungs remain inflamed even when you feel “recovered.”
This low-grade inflammation blocks regeneration and causes lingering symptoms like tightness, fatigue, and cough.
To reduce post-inflammatory stress:
-
Omega-3s — Lower inflammatory cytokines (found in salmon, chia seeds, walnuts).
-
Curcumin — Suppresses NF-κB signaling, the master switch of inflammation.
-
Vitamin D3 + K2 — Modulate immune balance and tissue repair.
-
Green tea catechins — Protect lung cells from oxidative damage.
Science says:
A BMJ (2024) study found that omega-3 supplementation reduced post-infection lung inflammation by 35% and accelerated oxygen recovery by 20%.
🧬 3. Antioxidant Defense and Cellular Renewal
The lungs are constantly exposed to oxygen — and thus, to oxidative stress.
Over time, free radicals damage cellular membranes and DNA.
To counter this, the body relies on antioxidant systems, particularly glutathione, superoxide dismutase (SOD), and catalase.
Foods that enhance antioxidant repair:
-
Broccoli sprouts (sulforaphane) — activates Nrf2 detox pathways.
-
Blueberries and pomegranate — rich in anthocyanins.
-
Garlic and onions — boost glutathione.
-
Green leafy vegetables — high in chlorophyll and magnesium.
Supplements to support regeneration:
-
N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) — precursor to glutathione; reduces mucus and oxidative damage.
-
Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) — restores antioxidant balance between cells.
-
CoQ10 — improves mitochondrial energy for tissue healing.
🫀 4. Restoring Circulation and Oxygen Flow
Healthy blood flow is essential for delivering oxygen and nutrients to lung tissue.
After illness, small blood vessels in the lungs (capillaries) can become constricted or inflamed.
Natural vasodilators and oxygen enhancers:
-
Beetroot juice — increases nitric oxide production, improving oxygen delivery.
-
Hawthorn berry — supports circulation and heart-lung synergy.
-
Magnesium — relaxes smooth muscles in the airways and arteries.
-
Gentle exercise — walking, yoga, or swimming enhances pulmonary perfusion.
Breathing tip:
Practice “pursed-lip breathing” — inhale through the nose for 2 seconds, exhale through pursed lips for 4 seconds.
This helps keep airways open longer, improving oxygen exchange in damaged tissue.
🌬️ 5. Healing Breathwork for Recovery
Once inflammation subsides, structured breathing exercises can rebuild lung elasticity and strength.
Recommended techniques:
-
Diaphragmatic breathing: Expands lower lobes of the lungs where most healing occurs.
-
4-6 relaxation breathing: Reduces nervous tension and improves oxygen efficiency.
-
Resonance breathing (5.5 breaths per minute): Synchronizes heart and lung rhythms for optimal oxygen uptake.
-
Humming breath: Vibrations stimulate nitric oxide release and soothe inflamed tissues.
Science says:
A Harvard Health (2023) trial on post-COVID patients showed daily breathwork improved lung capacity by 30% and reduced fatigue by half within six weeks.
🌿 6. The Role of Rest and Sleep in Regeneration
Lung tissue heals most effectively during deep sleep, when growth hormone levels rise and immune activity recalibrates.
During REM cycles, your breathing slows and deepens — stimulating repair and detoxification.
Sleep-enhancing habits:
-
Keep your room cool, dark, and free of synthetic fragrances.
-
Avoid screens 1 hour before bed — blue light inhibits melatonin.
-
Try magnesium glycinate or chamomile tea for relaxation.
-
Practice the 4-7-8 breathing technique before sleep to lower cortisol.
Healing happens when the body feels safe enough to rest.
💧 7. Hydration and Mucus Clearance
Hydration is critical to recovery — it keeps mucus thin and prevents congestion that can trap bacteria or toxins.
Aim for:
-
2–3 liters of water daily
-
Herbal teas with licorice, ginger, or thyme
-
Electrolytes from coconut water or sea salt
-
Steaming or humidifiers to moisten airways
Add a few drops of eucalyptus or peppermint oil to steam for a natural decongestant effect.
🍽️ 8. The Regenerative Meal Plan
Here’s a sample Lung Recovery Meal Plan designed to nourish cellular healing and reduce inflammation:
Breakfast:
Lunch:
Snack:
Dinner:
Each meal supports detox, oxygenation, and repair — with antioxidants, fiber, and clean proteins fueling regeneration.
🧘 9. Emotional Healing and Patience
Chronic illness often leaves emotional scars.
Anxiety, frustration, or grief about health can unconsciously tighten your breath — slowing physical recovery.
Mind-body techniques for emotional release:
-
Journaling about your healing process
-
Meditation or prayer for acceptance and calm
-
Gentle yoga to reconnect with your body
-
Gratitude practice: Shifts focus from illness to progress
Healing the lungs is not just physical — it’s emotional. Breath connects both worlds.
🌤️ 10. The Path Forward: Rebuilding Resilience
Recovery is not about returning to your old normal — it’s about building a stronger, wiser body.
Your lungs adapt, your cells learn, and your breath deepens with each day of conscious living.
Even small daily actions — a clean meal, a slow breath, a walk in nature — reinforce the cycle of renewal.
Your body is not broken. It is rebuilding.
Each breath you take is proof that healing is happening right now.
🔑 Key Takeaway
Lung regeneration is not a miracle — it’s a natural process that thrives when supported by clean air, nutrient-rich food, deep rest, and mindful breathwork.
The lungs can heal, the body can renew, and your breath can once again become a source of strength, not struggle.


by Rich Benvin | Oct 14, 2025 | Breathing, Detox, Healthcare, Integrative Medicine, Lifestyle Medicine, Mail Order Pharmacy, Respiratory Health, Save Your Lungs
Integrative Medicine & Modern Therapies — Combining Traditional Wisdom with Scientific Innovation for Lung Health
Breathe to Heal: How Nutrition and Lifestyle Can Save Your Lungs
“The future of medicine is not either-or — it’s everything that works.”
For decades, medicine has divided itself into camps: Western vs. Eastern, scientific vs. holistic, pharmaceutical vs. natural.
But the lungs don’t care about ideology — they respond to balance.
Integrative medicine brings together the best of both worlds.
It uses evidence-based therapies from modern science and time-tested healing practices from ancient traditions to restore harmony to the body’s natural systems.
For those with chronic respiratory challenges — asthma, COPD, post-viral inflammation, or long COVID — this blended approach can offer something extraordinary: not just symptom relief, but renewal.
🫁 1. The Functional Medicine View of Lung Health
Functional medicine looks for root causes, not just symptoms.
Rather than treating coughing or shortness of breath in isolation, it asks:
-
What’s triggering the inflammation?
-
Is the gut microbiome affecting immune response?
-
Is the body overloaded with toxins, allergens, or stress hormones?
By identifying the upstream factors — from nutrient deficiencies to environmental triggers — functional medicine helps patients achieve lasting recovery rather than temporary relief.
Core principles include:
-
Restoring balance to the gut-lung axis
-
Reducing inflammation through nutrition and lifestyle
-
Optimizing mitochondrial function for oxygen efficiency
-
Supporting detoxification and immune resilience
🌿 2. Traditional Herbal Medicine for Respiratory Healing
For centuries, herbal medicine has offered natural remedies for breathing difficulties — long before inhalers or antibiotics existed.
Many of these ancient herbs are now validated by modern research.
🌱 Top Herbal Allies for the Lungs:
| Herb |
Traditional Use |
Modern Science Insight |
| Mullein (Verbascum thapsus) |
Soothes dry coughs, clears mucus |
Contains saponins that help expel phlegm and reduce airway irritation |
| Licorice Root (Glycyrrhiza glabra) |
Anti-inflammatory, adrenal support |
Inhibits lung inflammation and protects against oxidative stress (Phytomedicine, 2023) |
| Lobelia (Indian Tobacco) |
Opens airways, eases asthma |
Contains lobeline — acts as a natural bronchodilator |
| Elecampane (Inula helenium) |
Treats chronic bronchitis and infections |
Contains alantolactone, which has antibacterial and expectorant effects |
| Nettle Leaf (Urtica dioica) |
Antihistamine, anti-allergy |
Reduces histamine response and supports immune modulation |
| Thyme & Oregano |
Antimicrobial and antiviral |
Rich in thymol and carvacrol — natural compounds that fight respiratory pathogens |
How to use:
These herbs can be taken as teas, tinctures, capsules, or in steam inhalations.
Always consult a practitioner if you’re on prescription medications, as some herbs may interact with pharmaceuticals.
🔬 3. Nutraceuticals and Supplements for Modern Lungs
Beyond herbs, many natural compounds are now backed by strong clinical evidence for respiratory support:
-
N-Acetylcysteine (NAC): Boosts glutathione, thins mucus, reduces oxidative stress.
-
Quercetin: Natural antihistamine that stabilizes mast cells and lowers inflammation.
-
Vitamin D3 + K2: Supports immune modulation and calcium balance in lung tissue.
-
Magnesium Glycinate: Relaxes bronchial muscles and improves airflow.
-
CoQ10 + Alpha-Lipoic Acid: Enhance mitochondrial energy for breathing efficiency.
-
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Anti-inflammatory and vascular support for oxygen delivery.
Science says:
A Johns Hopkins (2023) review found that combining omega-3s, NAC, and vitamin D reduced COPD flare-ups by 35% and improved lung function scores significantly compared to medication alone.
🩸 4. Acupuncture and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)
In Traditional Chinese Medicine, the lungs are known as the “delicate organ” — the interface between the external and internal worlds.
They’re associated with grief, immunity, and vitality.
Acupuncture aims to restore “Qi” (energy) flow through the lung meridians, reducing inflammation and improving oxygenation.
TCM Lung-Boosting Points:
-
LU-1 (Zhongfu): Opens the chest and clears congestion.
-
LU-9 (Taiyuan): Strengthens respiratory function and immunity.
-
ST-36 (Zusanli): Improves energy and digestion (gut-lung axis).
Evidence:
A Cochrane Review (2022) found that acupuncture reduced coughing and improved airflow in chronic bronchitis patients — particularly when combined with lifestyle interventions.
🌬️ 5. Oxygen and Light Therapies
Modern integrative clinics now use oxygen-based therapies and photobiomodulation to repair cellular damage in the lungs.
💨 Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT):
Patients breathe 100% oxygen in a pressurized chamber, delivering up to 10x more oxygen to tissues.
Benefits: Enhances healing after infection, reduces inflammation, promotes stem cell activity.
🔴 Red Light / Near-Infrared Therapy:
Penetrates skin and muscle to stimulate mitochondrial ATP production and reduce oxidative stress in lung tissue.
Science: Lasers in Medical Science (2024) found red light therapy improved oxygen saturation and lung recovery after COVID-related injury.
💧 Hydrogen Inhalation Therapy:
A new frontier in respiratory care — inhaling hydrogen gas (H₂) to neutralize oxidative radicals and calm inflammation.
Studies in Antioxidants (2023) show measurable improvements in COPD symptoms and endurance.
🌡️ 6. Breathing Devices and Biofeedback Tools
Technology is turning respiratory therapy into a home practice.
Top tools:
-
Spirometry apps — Track lung capacity and progress.
-
PEP devices (Positive Expiratory Pressure) — Strengthen lung muscles.
-
Biofeedback trainers — Help you visualize breath control and CO₂ balance.
-
Salt inhalers — Simulate halotherapy (salt therapy) to reduce mucus.
Using these tools for even 10 minutes daily can retrain breathing mechanics and improve oxygen utilization.
🧘 7. Mind-Body Healing: The Emotional Connection
In both Eastern and modern psychophysiology, the lungs are linked to emotion and grief.
Prolonged sadness, trauma, or anxiety can manifest physically as shallow breathing or tightness in the chest.
Integrative practices for emotional lung healing:
-
Breath-focused meditation for nervous system reset
-
Yoga and Qi Gong for restoring balance and energy flow
-
Sound therapy / humming exercises to activate the vagus nerve
-
Bodywork and somatic release for stored tension
Science continues to show that breath-centered mindfulness reduces anxiety, improves lung performance, and lowers systemic inflammation.
🧬 8. The Integrative Healing Model: A Holistic Blueprint
True respiratory healing happens when all dimensions — body, mind, nutrition, and environment — are aligned.
| Domain |
Modern Approach |
Holistic Complement |
| Nutrition |
Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant diet |
Ayurvedic herbs, lung-healing teas |
| Therapy |
Inhalers, medications |
Acupuncture, yoga, breathwork |
| Technology |
Oxygen therapy, air purifiers |
Nature walks, fresh air immersion |
| Mind |
Cognitive-behavioral therapy |
Meditation, emotional release practices |
Integration doesn’t replace medicine — it enhances it.
It transforms treatment from reaction to prevention, from survival to vitality.
🌈 9. The Future of Respiratory Medicine
The frontier of lung care is rapidly evolving.
Scientists are exploring stem-cell therapies, AI-guided respiratory diagnostics, and nanotechnology-based oxygen carriers that mimic natural red blood cells.
Yet, the most powerful innovations often return us to simplicity — the breath, the body, and balance.
As technology advances, it’s clear: the most sustainable medicine is one that restores our connection to nature and ourselves.
🌅 10. A New Paradigm of Healing
Imagine a world where hospitals prescribe meditation, nutrition plans, and fresh air therapy alongside inhalers and antibiotics.
Where breathwork is as routine as brushing your teeth, and preventive care is the foundation of medicine.
That’s not fantasy — it’s the direction healthcare is heading.
You are not a passive patient. You are an active participant in your healing.
Your lungs don’t just need medicine — they need meaning.
🔑 Key Takeaway
Integrative medicine unites the precision of modern science with the wisdom of ancient healing.
By combining herbs, nutrients, oxygen therapy, and mindfulness, you give your lungs the best of both worlds — natural resilience and scientific power.

by Rich Benvin | Oct 14, 2025 | Breathing, Detox, Environment, Lung Health, Respiratory Health, Save Your Lungs
Chapter 10: The Environment Factor — Air Quality, Pollution, and Protecting Your Lungs in a Modern World
Breathe to Heal: How Nutrition and Lifestyle Can Save Your Lungs
“You can’t choose the world you breathe in — but you can choose how you breathe through it.”
Every inhale connects you to the environment around you — for better or worse.
The average adult breathes about 20,000 times a day, drawing in roughly 11,000 liters of air.
That air isn’t just oxygen. It’s a mix of invisible elements — some healing, others harmful.
In today’s world, we face more environmental threats to lung health than at any other point in history.
From urban smog and wildfire smoke to indoor pollutants and microplastics, the respiratory system is constantly challenged.
But the good news is powerful: you have the ability to reduce your exposure, strengthen your defenses, and even reverse environmental damage — all through awareness, nutrition, and lifestyle.
☁️ 1. The Modern Air Crisis
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), over 90% of the global population lives in areas where air quality exceeds safe limits.
Air pollution now causes more than 7 million premature deaths each year — more than malaria, HIV, and car accidents combined.
The most dangerous pollutants include:
-
PM2.5: Microscopic particles from cars, industry, and fires that penetrate deep into the lungs.
-
Nitrogen dioxide (NO₂): Emitted by vehicles and gas stoves.
-
Ozone (O₃): A reactive gas that irritates lung tissue.
-
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs): Released by paints, cleaning products, and plastics.
These toxins trigger inflammation, oxidative stress, and cell damage — especially in people with asthma, COPD, or cardiovascular disease.
🏙️ 2. Outdoor Air: Invisible But Impactful
Whether you live in a city or rural area, outdoor air quality affects your health daily.
Urban dwellers are exposed to exhaust, ozone, and particulate matter, while rural residents may face pollen, dust, and agricultural chemicals.
Simple ways to reduce exposure:
-
Check local air quality indexes (AQI) using apps like AirNow or IQAir. Avoid outdoor exercise when AQI > 100.
-
Choose early morning walks when air is cooler and cleaner.
-
Use N95 masks during smog, wildfires, or heavy traffic exposure.
-
Plant greenery around your home: trees and houseplants naturally filter particulates.
-
Avoid idling vehicles or jogging near busy roads.
Science says:
A Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health (2024) study found that reducing daily PM2.5 exposure by just 10 µg/m³ cut mortality risk by 7% — a massive improvement achieved through simple behavioral changes.
🏠 3. Indoor Air: The Hidden Threat
Most people spend 90% of their lives indoors — yet indoor air can be 2 to 5 times more polluted than outdoor air.
Common indoor pollutants include:
-
Mold spores and dust mites (from humidity and poor ventilation)
-
Synthetic fragrances in candles, air fresheners, and detergents
-
Cleaning chemicals that release formaldehyde and VOCs
-
Gas stoves that emit nitrogen dioxide
-
Tobacco smoke and secondhand vapor
🧹 Steps to improve indoor air:
-
Ventilate daily. Open windows or use fans to circulate fresh air.
-
Use HEPA air purifiers — especially in bedrooms and living spaces.
-
Avoid synthetic fragrances. Choose essential oils or fragrance-free cleaners.
-
Control humidity (40–50%) to prevent mold growth.
-
Use nontoxic materials: natural cleaning agents like vinegar, lemon, or baking soda.
Pro tip: The NASA Clean Air Study identified peace lilies, spider plants, and snake plants as effective natural filters for VOCs and carbon monoxide.
🔥 4. Wildfire Smoke and Climate Challenges
In recent years, wildfire smoke has become one of the most severe threats to respiratory health — even for people hundreds of miles away from the flames.
Smoke contains ultra-fine particles and carcinogens that can linger in the air for weeks.
Protective measures:
-
Keep windows closed and use an indoor air purifier with activated carbon.
-
Wear a fit-tested N95 mask outdoors.
-
Avoid exercising or burning candles during smoke events.
-
Stay hydrated — water helps flush out toxins absorbed via inhalation.
-
Eat anti-inflammatory foods (turmeric, berries, green vegetables) to counter oxidative stress.
A 2023 Stanford Medicine report found that wildfire smoke exposure can age lung tissue by up to 10 years in frequent exposure zones — but that recovery is possible through antioxidant-rich diets and proper filtration.
🌿 5. The Role of Nutrition in Pollution Defense
You can’t stop breathing polluted air — but you can make your lungs more resilient to it.
The right nutrients strengthen your natural detox pathways and repair oxidative damage.
Top protective nutrients:
-
Vitamin C: Reduces airway inflammation and oxidative stress.
-
Vitamin E: Stabilizes cell membranes damaged by free radicals.
-
Sulforaphane (from broccoli sprouts): Activates detox enzymes that neutralize pollutants.
-
Omega-3 fatty acids: Decrease inflammatory cytokines caused by pollution exposure.
-
Flavonoids: Found in berries, onions, and apples — they strengthen lung capillaries.
Science says:
A British Medical Journal (2022) study showed that individuals with high fruit and vegetable intake had 30% better lung resilience during pollution spikes than those on low-plant diets.
🧴 6. The Chemical Load: Toxins in Everyday Products
It’s not just air pollution that harms the lungs — everyday household and beauty products also release harmful vapors.
Common offenders:
-
Aerosol sprays and disinfectants
-
Nail polish remover (acetone)
-
Perfumes and scented candles (phthalates, benzene)
-
Plastic containers (BPA, PVC)
Swap for cleaner options:
-
Use natural or unscented products.
-
Store food in glass, not plastic.
-
Use beeswax candles or diffusers instead of synthetic fragrances.
-
Choose non-toxic paints and cleaning supplies.
Over time, lowering your chemical load can reduce respiratory irritation, headaches, and fatigue.
🌬️ 7. Air Purification: Creating a Safe Breathing Zone
If the outside world is beyond your control, make your indoor environment your sanctuary.
How to purify your air naturally and effectively:
-
HEPA filters: Capture 99.97% of particles ≥0.3 microns (dust, pollen, smoke).
-
Activated carbon filters: Remove gases and odors.
-
Salt lamps or ionizers: Can help neutralize airborne particles.
-
Houseplants: Aloe vera, bamboo palm, and peace lilies naturally clean the air.
-
Charcoal bags: Passive air purifiers that absorb VOCs and moisture.
Tip: Replace air filters every 3 months — more often if you live in high-pollution zones.
🌈 8. Building Your “Clean Air Ritual”
Here’s how to turn environmental protection into a daily, effortless practice:
Morning:
-
Open windows briefly to flush out stale air.
-
Drink lemon water to hydrate and flush the respiratory tract.
-
Mist indoor plants to release oxygen and humidity.
Afternoon:
Evening:
-
Run your air purifier before bed.
-
Avoid candles, sprays, or strong detergents.
-
Do 10 minutes of deep breathing to clear residual CO₂ and relax the lungs.
Your home can be your greatest defense — a clean, oxygen-rich sanctuary for recovery.
🔬 9. The Future of Air and Lung Health
The intersection of climate change, urbanization, and industrialization makes clean air the next frontier of public health.
New technologies — like portable filtration systems, smart sensors, and air-quality wearables — are helping individuals monitor and protect their respiratory health in real time.
But the most powerful solution still lies within reach:
Supporting your body’s own resilience through mindful breathing, plant-rich nutrition, movement, and clean living.
The lungs are not passive victims of pollution — they are adaptive organs that can recover, rebuild, and thrive when given the right conditions.
🌤️ 10. A Breath of Empowerment
You may not control the air outside — but you can master the way your body interacts with it.
By making conscious choices about your environment, nutrition, and breathing, you turn every inhale into an act of protection.
Clean air begins within.
🔑 Key Takeaway
Air quality is one of the greatest health challenges of our era — but your lungs are powerful, regenerative, and responsive.
Through awareness, clean habits, and mindful breathing, you can transform even a polluted world into an opportunity for healing and renewal.


by Rich Benvin | Oct 14, 2025 | Breathing, Detox, Inflammation, Lifestyle Medicine, Lung Health, Mindfulness, Respiratory Health, Save Your Lungs
Chapter 8: Breathwork and Mindful Breathing Techniques — The Science of Healing Through Breath
Breathe to Heal: How Nutrition and Lifestyle Can Save Your Lungs
“Breath is the bridge between body and mind. Control the breath, and you control life itself.”
You can go without food for weeks, without water for days — but without breath, you last only minutes.
Yet most people go through life barely breathing at all.
We breathe shallowly, hurriedly, unconsciously — inhaling stress and exhaling exhaustion.
But hidden within this automatic process is the most powerful healing tool you possess: the ability to consciously reshape your biology, your emotions, and your mind through the act of breathing with awareness.
🧬 1. The Science Behind Conscious Breathing
When you take control of your breath, you’re not just changing airflow — you’re changing chemistry.
Every breath alters the ratio of oxygen and carbon dioxide (CO₂) in your blood.
This ratio determines your pH balance, heart rate, and even the messages your brain sends to your nervous system.
Slow, mindful breathing activates the parasympathetic nervous system — your body’s “rest and repair” mode.
Fast, shallow breathing triggers the sympathetic nervous system — the “fight or flight” response.
Through conscious breathing, you can literally flip this internal switch, moving from stress to calm, from inflammation to healing.
🫁 The Physiological Chain Reaction of Deep Breathing
Here’s what happens inside you during slow, diaphragmatic breathing:
-
The diaphragm expands downward, giving the lungs full range of motion.
-
Oxygen-rich air fills the lower lobes of the lungs — where most alveoli and blood vessels reside.
-
The vagus nerve is stimulated, lowering heart rate and calming the brain.
-
CO₂ levels balance, improving blood flow and oxygen delivery.
-
Nitric oxide levels increase, expanding airways and killing pathogens.
It’s not “woo-woo.” It’s biochemistry.
Breathwork doesn’t just relax you — it reprograms your nervous system to heal.
🌡️ 2. The Breath-Inflammation Connection
Chronic stress and shallow breathing keep the body locked in a low-grade inflammatory state.
High cortisol and adrenaline levels constrict airways, elevate blood pressure, and weaken immunity.
But studies from Harvard Medical School and the University of Wisconsin show that even 10 minutes of deep breathing per day can:
-
Reduce inflammatory markers like C-reactive protein (CRP) and IL-6
-
Increase antioxidant enzyme activity
-
Enhance immune resilience
The act of slowing down your breath tells your body: “I am safe.”
And safety is the signal your immune system needs to begin true repair.
🧘 3. Diaphragmatic Breathing — The Foundation Technique
The diaphragm is the primary muscle of respiration — yet most people rarely use it fully.
When you breathe from your chest, your shoulders rise and your lungs fill only halfway.
When you breathe from your diaphragm, your belly expands, and your lungs reach their full potential.
How to practice:
-
Sit or lie comfortably with one hand on your chest, one on your abdomen.
-
Inhale slowly through your nose for 4 seconds, feeling your belly rise.
-
Hold for 2 seconds.
-
Exhale through your mouth for 6 seconds, feeling your belly fall.
-
Repeat for 10–15 cycles.
Benefits:
-
Increases lung capacity
-
Improves oxygen efficiency
-
Relieves anxiety and muscle tension
-
Enhances digestion and sleep
Practice twice daily — once upon waking, once before bed.
🌬️ 4. Box Breathing — The Calm Under Pressure Technique
Originally developed by Navy SEALs, Box Breathing trains both focus and stress control.
How to practice:
-
Inhale through your nose for 4 counts.
-
Hold for 4 counts.
-
Exhale for 4 counts.
-
Hold again for 4 counts.
-
Repeat for 5–10 minutes.
Why it works:
This rhythmic breathing regulates CO₂ levels, enhances concentration, and resets your nervous system.
It’s especially useful during anxiety, panic, or high-stress moments.
Science says:
A Frontiers in Psychology (2023) study found that participants practicing Box Breathing daily experienced a 20% reduction in blood pressure and 30% decrease in perceived stress within two weeks.
❄️ 5. The Wim Hof Method — Awakening the Inner Oxygen Reserve
The Wim Hof Method combines controlled hyperventilation and cold exposure to increase oxygen saturation, stimulate mitochondria, and reduce inflammation.
Basic sequence:
-
Take 30 deep, rapid breaths — inhale fully, exhale halfway.
-
After the last exhale, hold your breath as long as comfortable.
-
Inhale deeply and hold for 15 seconds.
-
Repeat 3 rounds.
Benefits:
Note: This technique should be practiced safely, seated or lying down — never while driving or in water.
🌊 6. Alternate Nostril Breathing (Nadi Shodhana) — Balancing the Brain
An ancient yogic practice that harmonizes both hemispheres of the brain, balancing logic and intuition, effort and ease.
How to practice:
-
Sit comfortably. Close your right nostril with your thumb.
-
Inhale through the left nostril for 4 seconds.
-
Close the left nostril and exhale through the right for 6 seconds.
-
Reverse the process: inhale through right, exhale through left.
-
Continue for 5 minutes.
Benefits:
This simple technique can transform your energy within minutes.
💤 7. Breathing for Sleep and Recovery
Breathing influences sleep more than most people realize.
Rapid, irregular breathing keeps the nervous system alert — making deep rest impossible.
Try the 4-7-8 technique before bed:
-
Inhale through your nose for 4 seconds.
-
Hold for 7 seconds.
-
Exhale gently through your mouth for 8 seconds.
Repeat 5 times.
This pattern synchronizes your breath with your heart rate, releasing serotonin and melatonin naturally.
Result: lower cortisol, slower heartbeat, and a calm mind ready for sleep.
🧠 8. The Mind-Body Mechanism of Breath Awareness
When you consciously observe your breath, you activate the prefrontal cortex — the part of your brain responsible for awareness, decision-making, and emotional regulation.
This quiets the amygdala, your fear center, reducing anxiety and reactive behavior.
It’s the neurological foundation of meditation — and one reason why mindful breathing is used to treat PTSD, depression, and panic disorders worldwide.
Your breath is both the steering wheel and the compass of your nervous system.
🌤️ 9. Integrating Breathwork into Daily Life
The most powerful breathwork routine is the one you’ll actually use. Here are easy ways to weave mindful breathing into your day:
-
Morning reset: 10 deep belly breaths before checking your phone.
-
Before meals: 5 slow breaths to activate the parasympathetic system and improve digestion.
-
During stress: 4-6 breathing (inhale 4, exhale 6) to reduce cortisol.
-
Before sleep: 4-7-8 technique for relaxation.
Think of these as micro-meditations — small, mindful pauses that bring your body back into balance throughout the day.
🌈 10. The Breath as Medicine
Modern science is finally validating what ancient traditions have known for centuries:
The breath is the most accessible form of medicine.
It strengthens the lungs, lowers blood pressure, enhances immunity, and rewires the brain for resilience.
Unlike pharmaceuticals, it’s free, immediate, and personalized — tuned perfectly to your own biology.
You carry your pharmacy within you.
Every inhale is nourishment; every exhale, release.
🔑 Key Takeaway
Breathwork is the meeting point of body, mind, and healing.
By practicing diaphragmatic, rhythmic, and mindful breathing daily, you can calm inflammation, expand lung capacity, and cultivate a deeper connection to life itself — one breath at a time.
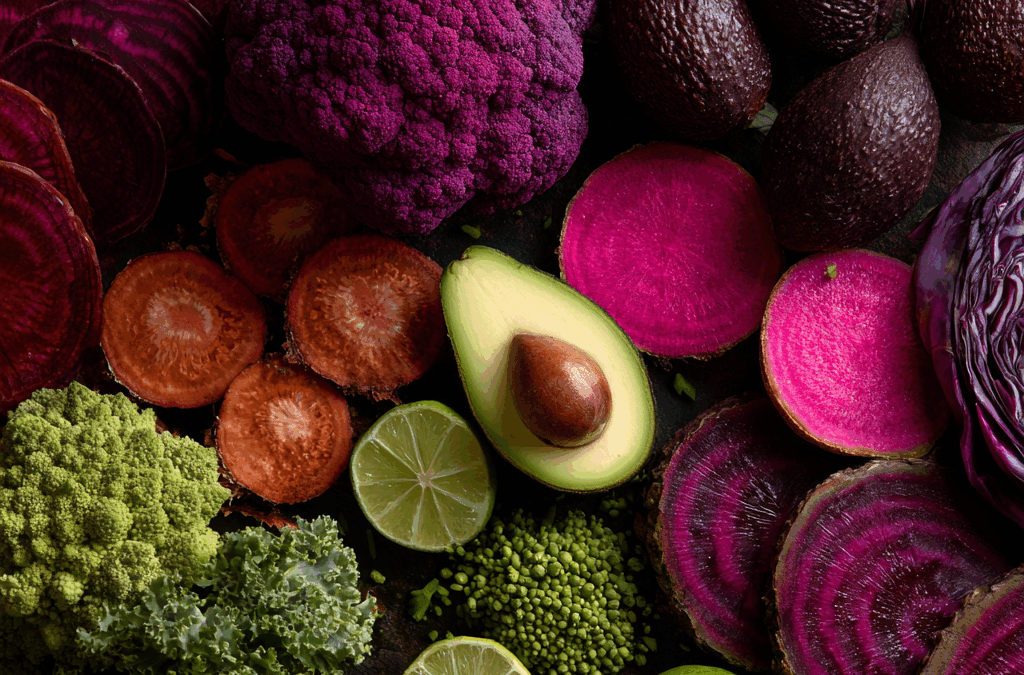


by Rich Benvin | Oct 14, 2025 | Detox, Inflammation, Lifestyle Medicine, Lung Health, Nutrition, Respiratory Health, Save Your Lungs
Chapter 5: The Power of Phytonutrients — How Plant Compounds Protect and Repair Lung Tissue
Breathe to Heal: How Nutrition and Lifestyle Can Save Your Lungs
“Every color on your plate is a molecule of medicine.”
The human lung is a marvel of biological design — delicate, efficient, and astonishingly responsive to its environment.
And while modern medicine often looks to synthetic drugs for protection, nature has quietly been offering us an arsenal of healing compounds for millennia.
These natural molecules, called phytonutrients or phytochemicals, are found in fruits, vegetables, herbs, and teas.
They’re not vitamins or minerals — they’re the plant’s own defense system against stress, sunlight, and disease.
When we eat them, we inherit those defenses.
In the past decade, hundreds of studies have shown that phytonutrients protect lung tissue, calm inflammation, and even help the body detoxify pollutants.
They are nature’s anti-inflammatory pharmacy — and they work in synergy with your body’s own healing systems.
🌈 1. How Phytonutrients Work in the Body
When you eat colorful plant foods — think blueberries, kale, turmeric, or green tea — your body absorbs thousands of bioactive compounds that interact with your cells.
Phytonutrients work by:
-
Neutralizing free radicals that damage lung cells.
-
Modulating immune responses, keeping inflammation in check.
-
Activating detox enzymes that help eliminate toxins from the bloodstream.
-
Repairing DNA and supporting cellular regeneration.
The result: lower oxidative stress, stronger airways, and improved lung function — all achieved through daily food choices rather than pharmaceuticals.
In short, phytonutrients don’t suppress your symptoms — they upgrade your biology.
🍇 2. The Colors of Healing: What Each Hue Means for Your Lungs
Each color in nature’s palette represents a family of specific phytonutrients. Eating across the color spectrum is one of the simplest ways to nourish your lungs on a molecular level.
| Color |
Key Compounds |
Lung Health Benefits |
Best Sources |
| 🟥 Red |
Lycopene, anthocyanins |
Reduces oxidative damage, supports blood flow |
Tomatoes, cherries, raspberries |
| 🟧 Orange |
Beta-carotene, zeaxanthin |
Boosts lung elasticity, supports mucosal lining |
Carrots, sweet potatoes, oranges |
| 🟨 Yellow |
Flavonoids, lutein |
Protects airway cells from toxins |
Lemons, bell peppers, turmeric |
| 🟩 Green |
Chlorophyll, sulforaphane |
Detoxifies and reduces inflammation |
Kale, broccoli, spinach |
| 🟪 Purple/Blue |
Resveratrol, anthocyanins |
Enhances circulation, protects DNA |
Blueberries, grapes, purple cabbage |
Each meal you color is a dose of cellular resilience.
🧬 3. Star Players in Lung Protection
Let’s dive into the research-backed superstars of the phytonutrient world — the compounds shown to have direct respiratory benefits.
🌱 Quercetin — The Natural Antihistamine
How it works:
Quercetin is a flavonoid found in onions, apples, capers, and berries. It stabilizes mast cells — immune cells that release histamine during allergic reactions — helping reduce airway inflammation and allergic asthma.
Science says:
A Frontiers in Immunology (2023) review found quercetin decreases airway hyper-responsiveness and improves breathing in asthma patients.
Best food sources:
Red onions, apples, kale, berries, and green tea.
🥦 Sulforaphane — The Detox Master
How it works:
Found in cruciferous vegetables (especially broccoli sprouts), sulforaphane activates the Nrf2 pathway — the body’s main antioxidant defense system.
It boosts detoxification enzymes in the lungs and liver, helping clear pollutants, heavy metals, and carcinogens.
Science says:
A Johns Hopkins University study showed that participants who consumed broccoli sprout extract excreted 60% more air pollutants through urine than those who didn’t.
Best food sources:
Broccoli sprouts, kale, Brussels sprouts, cabbage.
🍷 Resveratrol — The Longevity Molecule
How it works:
Resveratrol, found in red grapes and blueberries, protects lung tissue by reducing oxidative stress and fibrosis (scarring). It also improves mitochondrial efficiency — enhancing the lungs’ energy production.
Science says:
Studies in The Journal of Respiratory Research show resveratrol can reduce inflammatory cytokines and prevent progression in chronic bronchitis models.
Best food sources:
Red grapes, blueberries, cranberries, peanuts, dark chocolate.
🍵 Catechins — The Antioxidant Powerhouse
How it works:
Catechins (especially EGCG) are polyphenols found in green tea. They inhibit inflammatory pathways and may protect against lung cancer development.
Science says:
Green tea drinkers show 20% lower rates of chronic respiratory disease, according to a large-scale Japanese study (Epidemiology Journal, 2022).
Best food sources:
Green tea, matcha, white tea, apples.
🌶️ Curcumin — The Inflammation Modulator
How it works:
The golden pigment in turmeric, curcumin, is one of the most studied natural anti-inflammatories. It suppresses NF-κB — the molecular “switch” that triggers chronic inflammation in the lungs.
Science says:
Clinical trials have shown curcumin supplementation reduces COPD flare-ups and improves lung function (American Thoracic Society Review, 2023).
Best food sources:
Turmeric (paired with black pepper to boost absorption), curry, golden milk.
🌰 Ellagic Acid — The Cellular Guardian
How it works:
Found in pomegranates and walnuts, ellagic acid neutralizes carcinogens and protects DNA from mutation caused by pollution and smoking.
Science says:
A 2024 study in Nutrients found ellagic acid reduced oxidative stress in smokers by 45% within eight weeks.
Best food sources:
Pomegranates, raspberries, walnuts.
🫀 4. Synergy Matters — Why Whole Foods Beat Supplements
It can be tempting to buy a dozen antioxidant supplements, but the truth is: whole foods work better.
In nature, phytonutrients coexist with fiber, enzymes, and cofactors that enhance absorption and balance their effects.
For example, vitamin C boosts quercetin absorption; healthy fats improve carotenoid uptake; and polyphenols in tea work best with plant-based meals.
Your body recognizes food — not isolated chemicals.
Think of your diet as a symphony of molecules. The more colorful and varied your meals, the more harmonious your biology becomes.
🍽️ 5. Practical Ways to Eat More Phytonutrients
Here’s how to bring this science into daily life:
-
Eat the Rainbow: Aim for five colors at every meal.
-
Blend, Don’t Juice: Smoothies preserve fiber and maximize nutrient synergy.
-
Add Herbs and Spices: Turmeric, oregano, basil, and thyme are potent phytonutrient sources.
-
Steam, Don’t Fry: Light steaming preserves antioxidants in vegetables.
-
Swap White for Green: Trade refined grains for leafy sides — spinach, kale, or bok choy.
-
Drink Smart: Replace one coffee with green tea or herbal infusions daily.
Over time, these small, consistent actions saturate your body with plant-based compounds that help your lungs function optimally — from detoxification to repair.
💨 6. Nature’s Toolkit Against Modern Pollution
We can’t always control the air outside, but we can fortify the inside.
Regular consumption of phytonutrient-rich foods has been shown to:
-
Lower blood levels of inflammatory markers like CRP.
-
Increase antioxidant enzyme production in the lungs.
-
Reduce DNA damage from smoke and urban pollution.
-
Improve respiratory endurance in athletes and patients alike.
When you eat this way, your body becomes a living air purifier — filtering toxins, repairing damage, and exhaling strength.
🌿 7. Sample Phytonutrient-Rich Meal Ideas
Breakfast:
-
Spinach omelet with turmeric, black pepper, and tomatoes
-
Green tea with lemon and honey
Lunch:
-
Quinoa bowl with roasted broccoli, kale, and pomegranate seeds
-
Fresh-squeezed carrot-ginger juice
Snack:
Dinner:
-
Grilled salmon with garlic and herbs
-
Steamed Brussels sprouts with olive oil
-
Berry compote for dessert
Bonus: Sprinkle turmeric or cinnamon into smoothies or soups — every pinch adds protection.
🔑 Key Takeaway
Phytonutrients are the plant kingdom’s secret weapon — powerful natural compounds that protect, repair, and rejuvenate the lungs. Eating a rainbow of whole foods daily is one of the most effective ways to breathe stronger, live longer, and heal from the inside out.










