How Plant Compounds Protect and Repair Lung Tissue – Ch 5 – Breathe to Heal: How Nutrition and Lifestyle Can Save Your Lungs
Chapter 5: The Power of Phytonutrients — How Plant Compounds Protect and Repair Lung Tissue
Breathe to Heal: How Nutrition and Lifestyle Can Save Your Lungs
“Every color on your plate is a molecule of medicine.”
The human lung is a marvel of biological design — delicate, efficient, and astonishingly responsive to its environment.
And while modern medicine often looks to synthetic drugs for protection, nature has quietly been offering us an arsenal of healing compounds for millennia.
These natural molecules, called phytonutrients or phytochemicals, are found in fruits, vegetables, herbs, and teas.
They’re not vitamins or minerals — they’re the plant’s own defense system against stress, sunlight, and disease.
When we eat them, we inherit those defenses.
In the past decade, hundreds of studies have shown that phytonutrients protect lung tissue, calm inflammation, and even help the body detoxify pollutants.
They are nature’s anti-inflammatory pharmacy — and they work in synergy with your body’s own healing systems.
🌈 1. How Phytonutrients Work in the Body
When you eat colorful plant foods — think blueberries, kale, turmeric, or green tea — your body absorbs thousands of bioactive compounds that interact with your cells.
Phytonutrients work by:
-
Neutralizing free radicals that damage lung cells.
-
Modulating immune responses, keeping inflammation in check.
-
Activating detox enzymes that help eliminate toxins from the bloodstream.
-
Repairing DNA and supporting cellular regeneration.
The result: lower oxidative stress, stronger airways, and improved lung function — all achieved through daily food choices rather than pharmaceuticals.
In short, phytonutrients don’t suppress your symptoms — they upgrade your biology.
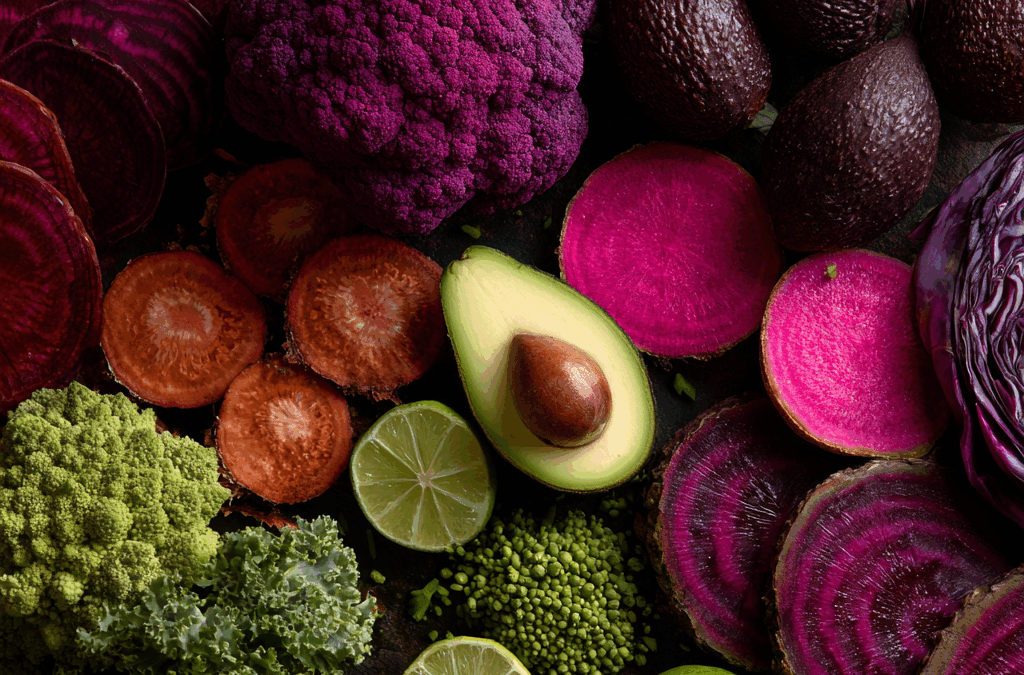
🍇 2. The Colors of Healing: What Each Hue Means for Your Lungs
Each color in nature’s palette represents a family of specific phytonutrients. Eating across the color spectrum is one of the simplest ways to nourish your lungs on a molecular level.
| Color | Key Compounds | Lung Health Benefits | Best Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🟥 Red | Lycopene, anthocyanins | Reduces oxidative damage, supports blood flow | Tomatoes, cherries, raspberries |
| 🟧 Orange | Beta-carotene, zeaxanthin | Boosts lung elasticity, supports mucosal lining | Carrots, sweet potatoes, oranges |
| 🟨 Yellow | Flavonoids, lutein | Protects airway cells from toxins | Lemons, bell peppers, turmeric |
| 🟩 Green | Chlorophyll, sulforaphane | Detoxifies and reduces inflammation | Kale, broccoli, spinach |
| 🟪 Purple/Blue | Resveratrol, anthocyanins | Enhances circulation, protects DNA | Blueberries, grapes, purple cabbage |
Each meal you color is a dose of cellular resilience.
🧬 3. Star Players in Lung Protection
Let’s dive into the research-backed superstars of the phytonutrient world — the compounds shown to have direct respiratory benefits.
🌱 Quercetin — The Natural Antihistamine
How it works:
Quercetin is a flavonoid found in onions, apples, capers, and berries. It stabilizes mast cells — immune cells that release histamine during allergic reactions — helping reduce airway inflammation and allergic asthma.
Science says:
A Frontiers in Immunology (2023) review found quercetin decreases airway hyper-responsiveness and improves breathing in asthma patients.
Best food sources:
Red onions, apples, kale, berries, and green tea.
🥦 Sulforaphane — The Detox Master
How it works:
Found in cruciferous vegetables (especially broccoli sprouts), sulforaphane activates the Nrf2 pathway — the body’s main antioxidant defense system.
It boosts detoxification enzymes in the lungs and liver, helping clear pollutants, heavy metals, and carcinogens.
Science says:
A Johns Hopkins University study showed that participants who consumed broccoli sprout extract excreted 60% more air pollutants through urine than those who didn’t.
Best food sources:
Broccoli sprouts, kale, Brussels sprouts, cabbage.
🍷 Resveratrol — The Longevity Molecule
How it works:
Resveratrol, found in red grapes and blueberries, protects lung tissue by reducing oxidative stress and fibrosis (scarring). It also improves mitochondrial efficiency — enhancing the lungs’ energy production.
Science says:
Studies in The Journal of Respiratory Research show resveratrol can reduce inflammatory cytokines and prevent progression in chronic bronchitis models.
Best food sources:
Red grapes, blueberries, cranberries, peanuts, dark chocolate.
🍵 Catechins — The Antioxidant Powerhouse
How it works:
Catechins (especially EGCG) are polyphenols found in green tea. They inhibit inflammatory pathways and may protect against lung cancer development.
Science says:
Green tea drinkers show 20% lower rates of chronic respiratory disease, according to a large-scale Japanese study (Epidemiology Journal, 2022).
Best food sources:
Green tea, matcha, white tea, apples.
🌶️ Curcumin — The Inflammation Modulator
How it works:
The golden pigment in turmeric, curcumin, is one of the most studied natural anti-inflammatories. It suppresses NF-κB — the molecular “switch” that triggers chronic inflammation in the lungs.
Science says:
Clinical trials have shown curcumin supplementation reduces COPD flare-ups and improves lung function (American Thoracic Society Review, 2023).
Best food sources:
Turmeric (paired with black pepper to boost absorption), curry, golden milk.
🌰 Ellagic Acid — The Cellular Guardian
How it works:
Found in pomegranates and walnuts, ellagic acid neutralizes carcinogens and protects DNA from mutation caused by pollution and smoking.
Science says:
A 2024 study in Nutrients found ellagic acid reduced oxidative stress in smokers by 45% within eight weeks.
Best food sources:
Pomegranates, raspberries, walnuts.
🫀 4. Synergy Matters — Why Whole Foods Beat Supplements
It can be tempting to buy a dozen antioxidant supplements, but the truth is: whole foods work better.
In nature, phytonutrients coexist with fiber, enzymes, and cofactors that enhance absorption and balance their effects.
For example, vitamin C boosts quercetin absorption; healthy fats improve carotenoid uptake; and polyphenols in tea work best with plant-based meals.
Your body recognizes food — not isolated chemicals.
Think of your diet as a symphony of molecules. The more colorful and varied your meals, the more harmonious your biology becomes.
🍽️ 5. Practical Ways to Eat More Phytonutrients
Here’s how to bring this science into daily life:
-
Eat the Rainbow: Aim for five colors at every meal.
-
Blend, Don’t Juice: Smoothies preserve fiber and maximize nutrient synergy.
-
Add Herbs and Spices: Turmeric, oregano, basil, and thyme are potent phytonutrient sources.
-
Steam, Don’t Fry: Light steaming preserves antioxidants in vegetables.
-
Swap White for Green: Trade refined grains for leafy sides — spinach, kale, or bok choy.
-
Drink Smart: Replace one coffee with green tea or herbal infusions daily.
Over time, these small, consistent actions saturate your body with plant-based compounds that help your lungs function optimally — from detoxification to repair.
💨 6. Nature’s Toolkit Against Modern Pollution
We can’t always control the air outside, but we can fortify the inside.
Regular consumption of phytonutrient-rich foods has been shown to:
-
Lower blood levels of inflammatory markers like CRP.
-
Increase antioxidant enzyme production in the lungs.
-
Reduce DNA damage from smoke and urban pollution.
-
Improve respiratory endurance in athletes and patients alike.
When you eat this way, your body becomes a living air purifier — filtering toxins, repairing damage, and exhaling strength.
🌿 7. Sample Phytonutrient-Rich Meal Ideas
Breakfast:
-
Spinach omelet with turmeric, black pepper, and tomatoes
-
Green tea with lemon and honey
Lunch:
-
Quinoa bowl with roasted broccoli, kale, and pomegranate seeds
-
Fresh-squeezed carrot-ginger juice
Snack:
-
Handful of walnuts and blueberries
Dinner:
-
Grilled salmon with garlic and herbs
-
Steamed Brussels sprouts with olive oil
-
Berry compote for dessert
Bonus: Sprinkle turmeric or cinnamon into smoothies or soups — every pinch adds protection.
🔑 Key Takeaway
Phytonutrients are the plant kingdom’s secret weapon — powerful natural compounds that protect, repair, and rejuvenate the lungs. Eating a rainbow of whole foods daily is one of the most effective ways to breathe stronger, live longer, and heal from the inside out.